Advanced MRI imaging
There are several advanced MRI techniques for more sophisticated imaging of brain structure and function. The most common advanced imaging techniques include spectroscopy, perfusion, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and functional MRI (fMRI). This page gives some of the details of using advanced imaging techniques for brain imaging and surgical planning.
MRI Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
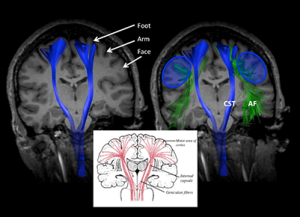
Diffusion tensor imaging, or DTI, is an advanced MRI technique in which the asymmetric motion of water is used to map out specific properties in the brain. One application of DTI is called tractography, or identifying the specific tracts of neurons which pass through the brain.
Locating the corticospinal tract (CST)
One of the most important fiber tracts in the brain is the corticospinal tract, or CST. This tract connects the motor cortex with the spinal cord, passing through the cerebral peduncles. This fiber tract is important because it is the tract most responsible for voluntary movement. It can be affected by a number of pathologies, such as tumors, cortical malformation, and stroke. For some conditions, such as tumors, it can be critically important to locate the CST before performing surgery, so that the surgeons can properly plan their surgery. That’s where DTI comes in.
To identify the corticospinal tract, you can use a two region of interest method, first placing a region of interest in the cerebral peduncle and a second in the motor cortex. To learn more about this method and the potential pitfalls, watch the video.
Functional MRI (fMRI)
Blood oxygen level dependent functional MRI, or BOLD fMRI, is an advanced MRI technique in which level of oxygen present in an area of the brain is used to map out what parts of the brain are activated in specific tasks. In this method, repeated imaging of the brain can be performed while the patient performs a task, and the level of oxygenation changes, showing which parts of the brain are most activated.
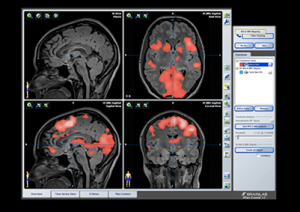
Brainlab Processing Guide
A key application of fMRI is mapping of language areas, or language localization, for surgical planning. The patient will perform more than 1 language task while in the scanner, and the activation data is overlaid on anatomic imaging (like conventional T1 or T1 postcontrast imaging). This is used to determine which side of the brain is language dominant as well as where exactly important language areas, including Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas, are located. This way they can be avoided in complex surgical procedures. However, sometimes results can be difficult to interpret because of the high number of images and high amounts of noise.
There are a number of processing suites that you can use to process fMRI data, including Brainlab and Dynasuite. The processing can be slightly different depending on which software package you are using, but the general principles are the same. To begin, you take each functional paradigm and overlay it on anatomical imaging, selecting statistical parameters and colormapping as you go.
To learn more about fMRI processing with Brainlab, watch the video with Dr. Hoch explaining the step-by-step process of generating each set of overlay imaging and how to interpret the results. In the second part of the video, he demonstrates conjunction overlay technique to increase sensitivity for mapping language areas by showing only the areas which have overlapping results on multiple paradigms, increasing reader confidence.
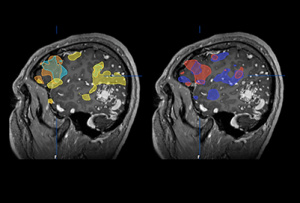
Language localization – conjunction display
When localizing language areas, sometimes results can be difficult to interpret because of the high number of images and high amounts of noise. One way to mitigate this is by overlaying all language paradigms on a single set of images using different colors. This increases the visibility of otherwise hard to see areas, increasing reader confidence.
To learn more about language localization with fMRI conjunction display, check out the video.
Learn more
To learn more, check out the whole video playlist on advanced MRI imaging or the entire Learnneuroradiology youtube channel.